GONORRHEA
GONORRHEA IS…
- A common sexually transmitted disease (STD).
- Caused by bacteria.
- Sometimes called “the clap” or “the drip”.
- Easily treated soon after infection, but may cause lifelong complications (especially in women) if not diagnosed and treated early.
HOW IS GONORRHEA SPREAD?
Gonorrhea spreads by vaginal, oral or anal sex with an infected person, even if that person has no symptoms. It can also be passed from a mother to her baby during birth.
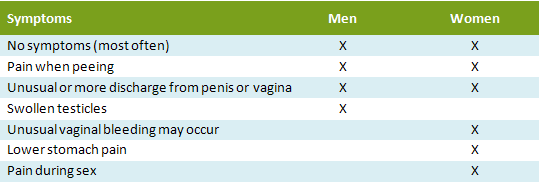
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF GONORRHEA?
HOW DO YOU GET TESTED FOR GONORRHEA?
A healthcare provider can do tests to see if you have gonorrhea, even if you don’t have symptoms. Many providers can now test for this infection with a urine sample, but other tests might be necessary. Not all healthcare providers will test you for gonorrhea without being asked to, so be sure to ask your healthcare provider to have this test done. Let your healthcare provider know the best way to confidentially reach you with test results.
CAN GONORRHEA BE TREATED?
Several types of antibiotics can cure gonorrhea; however, drug-resistant infections are increasing. You can get gonorrhea again even after you have been treated, so it is very important to get your partner(s) tested and treated so you don’t get re-infected and the infection doesn’t spread to others.
WHAT HAPPENS IF YOU DON’T GET TREATMENT?
- In women, the infection can move into other parts of the reproductive system and cause scarring, which increases the chance that she may have trouble getting pregnant in the future- this is called pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). A woman who has gonorrhea can pass it to her baby during the birth process, which can cause eye infections that can cause blindness and other health problems.
- In men, the infection can spread to the testicles, causing them to swell and become painful. This can create scar tissue that might affect their ability to father a child in the future.
- In both men and women, untreated gonorrhea can affect other organs and parts of the body including the throat, eyes, heart, brain, skin and joints, although this is less common.
WHAT IF YOU’RE DIAGNOSED WITH GONORRHEA?
If a healthcare provider diagnoses you with gonorrhea, they should prescribe an antibiotic for you to take. You will also need to tell your partner(s) so that they can be tested and treated.
A partner with whom you’ve had unprotected sex with will likely be infected too, so it’s important for both of you to receive treatment so that you don’t pass the infection back and forth between one another or to others.
Even if you don’t plan to have sex with your partner(s) again, it’s important they are told so that the infection doesn’t spread to anybody else. In addition to you and your partner receiving treatment, you should not have any sex for 7-10 days after you and your partner finish the treatment.
If you need help telling your partner about the infection, click here for helpful ways to handle the discussion.
IS GONORRHEA PREVENTABLE?
The surest way to avoid a gonorrhea infection is to avoid any activity that passes sexual fluids. If you decide to have sex, choose to be in a relationship where you and your partner only have sex with each other and use latex or polyurethane condoms correctly and every time you have sex.
Make sure you’re correctly using condoms, check out the how to use a condom video. For women who are pregnant, the best way to prevent spreading the infection to the baby is to get treated as quickly as possible, treat sex partners, and have a retest to ensure the bacteria is completely gone before giving birth.



